Speech recognition refers to a computer interpreting the words spoken by a person and converting them to a format that is understandable by a machine. Depending on the end goal, it is then converted to text or voice, or another required format. For instance, Apple’s Siri and Google’s Alexa use AI-powered speech recognition to provide voice or text support whereas voice-to-text applications like Google Dictate transcribe your dictated words to text.
Speech recognition AI applications have seen significant growth in numbers in recent times as businesses are increasingly adopting digital assistants and automated support to streamline their services. Voice assistants, smart home devices, search engines, etc are a few examples where speech recognition has seen prominence.
Data is required to train a speech recognition model because it allows the model to learn the relationship between the audio recordings and the transcriptions of the spoken words. By training on a large dataset of audio recordings and corresponding transcriptions, the model can learn to recognize patterns in the audio that correspond to different words and phonemes (speech sounds).
For example, if the model is trained on a large dataset of audio recordings of people speaking English, it will learn to recognize common patterns in the audio that corresponds to English words and phonemes. These patterns might include the frequency spectrum of different phonemes, the duration of different vowel and consonant sounds, and the context in which different words are used. By learning these patterns, the model can then take as input a new audio recording and use what it has learned to transcribe the spoken words in the audio. Without a large and diverse dataset of audio recordings and transcriptions, the model would not have enough data to learn these patterns and would not be able to perform speech recognition accuracy.
What is speech recognition data?
Speech recognition data refers to audio recordings of human speech used to train a voice recognition system. This audio data is typically paired with a text transcription of the speech, and language service providers are well-positioned to help.
The audio and transcription are fed to a machine-learning algorithm as training data. That way, the system learns how to identify the acoustics of certain speech sounds and the meaning behind the words.
There are many readily available sources of speech data, including public speech corpora or pre-packaged datasets, but in most cases, you will need to work with a data services provider to collect your own speech data through the remote collection or in-person collection. You can customize your speech dataset by variables like language, speaker demographics, audio requirements, or collection size.
The data collected need to be annotated for further training of the speech recognition model.
What is Speech or Audio Annotation?
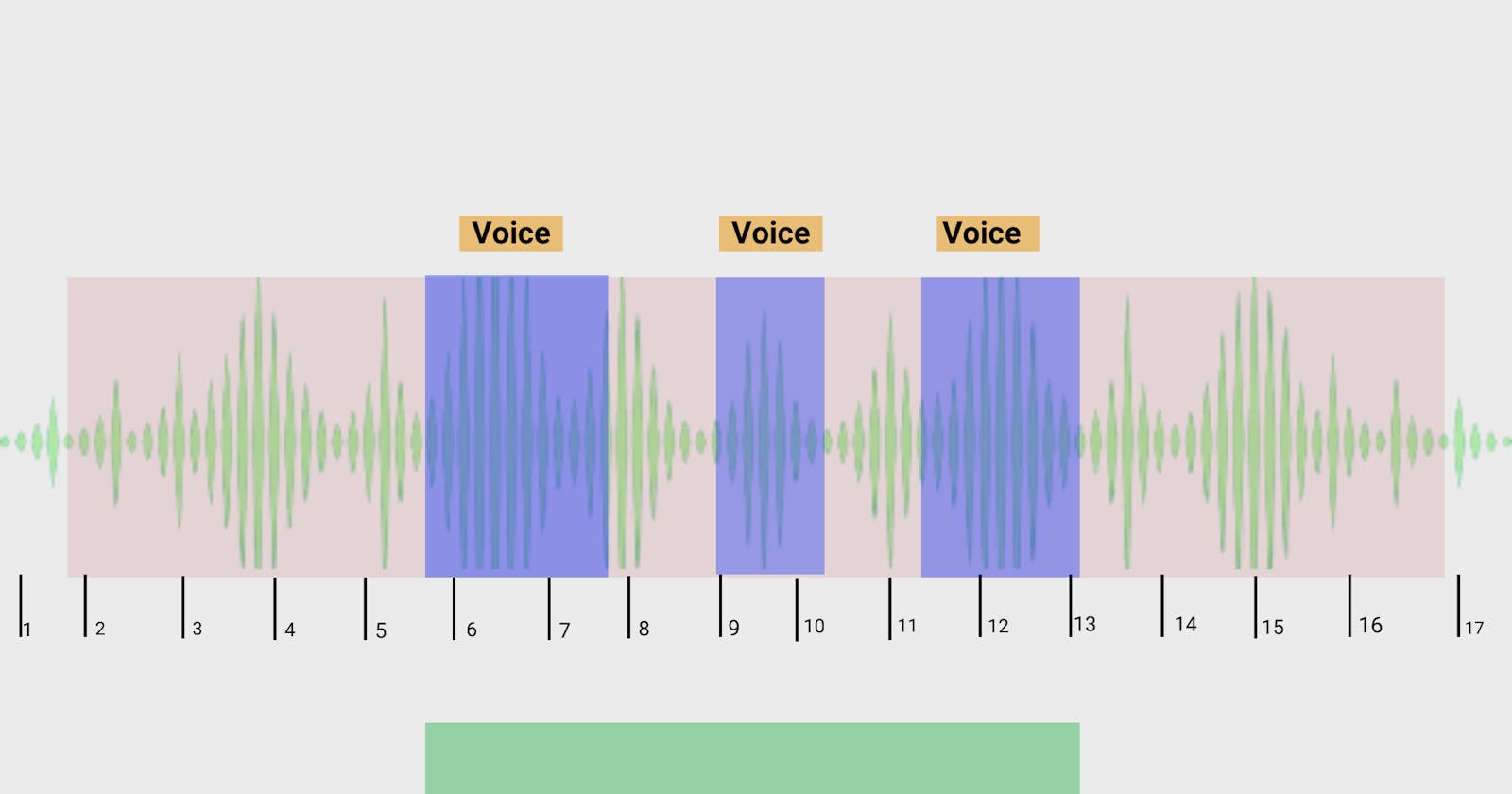
For any system to understand human speech or voice, it requires the use of artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning. Machine learning models that are developed to react to human speech or voice commands need to be trained to recognize specific speech patterns. The large volume of audio or speech data required to train such systems needs to go through an annotation or labeling process first, rather than being ingested in a raw audio file.
Effectively, audio or speech annotation is the technique that enables machines to understand spoken words, human emotions, sentiments, and intentions. Just like other types of annotations for image and video, audio annotation requires manual human effort where data labeling experts can tag or label specific parts of audio or speech clips being used for machine learning. One common misconception is that audio annotations are simply audio transcriptions, which are the result of converting spoken words into written words. Audio annotation goes beyond audio transcription, adding labeling to each relevant element of the audio clips being transcribed.
Speech annotation is the process of adding metadata to spoken language data. This metadata can include a transcription of the spoken words, as well as information about the speaker’s gender, age, accent, and other characteristics. Speech annotation is often used to create training data for natural language processing and speech recognition systems.
There are several different types of speech or audio annotation, including:
Transcription:
The process of transcribing spoken words into written text.
Part-of-speech tagging:
The process of identifying and labeling the parts of speech in a sentence, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives.
Named entity recognition:
The process of identifying and labeling proper nouns and other named entities in a sentence, such as people, organizations, and locations.
Dialog act annotation:
The process of labeling the types of actions that are being performed in a conversation, such as asking a question or making a request.
Speaker identification:
The process of identifying and labeling the speaker in an audio recording.
Speech emotion recognition:
The process of identifying and labeling emotions that are expressed through speech, such as happiness, sadness, or anger.
Acoustic event detection:
The process of identifying and labeling specific sounds or events in an audio recording, such as the sound of a car horn or the sound of a person speaking.
These are just a few examples of the types of speech or audio annotation that can be performed. The specific types of annotation that are used will depend on the needs and goals of the natural language processing or speech recognition system being developed. Speech annotation can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, but it is an important step in the development of many natural language processing and speech recognition systems.
How to Annotate Speech Data
To perform audio annotation, organizations can use software currently available in the market. Free and open-source annotation tools exist that can be customized for your business needs. Alternatively, you can opt for paid annotation tools that have a range of features to support different types of annotation. Such paid annotation tools are generally supported by a team of professionals, who can configure the tool for your purpose. Another option would be to develop your own customized annotation tool within your organization. However, this can be slow and expensive and requires you to have an in-house team of annotation experts.
Companies that do not want to spend their resources on in-house annotation, can opt to outsource their work to an external service provider specializing in the annotation. Outsourcing may be the best choice for your organization, because service providers:
have a team of available data experts who are skilled in the time-intensive tasks of data cleaning and preparation that are required prior to data annotation
can often start immediately executing the type of labeling that your business needs
deliver high-quality data for your machine learning models and requirements
accelerate the scaling (and ROI) of your resource-intensive annotation initiatives
Use Cases of Speech Recognition
Speech recognition is a technology that allows computers to understand and interpret human speech. It has a wide range of applications, including:
Voice assistants:
Speech recognition is used in voice assistants, such as Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa, to allow users to interact with their devices using voice commands.
Dictation software:
Speech recognition can be used to transcribe spoken words into written text, making it easier for people to create documents and emails.
Customer service:
Speech recognition is used in customer service centers to allow customers to interact with automated systems using voice commands.
Education:
Speech recognition can be used to provide feedback to students on their pronunciation and speaking skills.
Healthcare:
Speech recognition is used in healthcare settings to transcribe doctors’ notes and to allow patients to interact with their electronic health records using voice commands.
Transportation:
Speech recognition is used in self-driving cars to allow passengers to give voice commands to the vehicle.
Home automation:
Speech recognition is used in smart home systems to allow users to control their appliances and devices using voice commands.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of speech recognition technology. It has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with computers and other devices, making it easier and more convenient for people to communicate with them.
Conclusion
With natural language processing (NLP) becoming more mainstream across business enterprises, the need for high-quality audio annotation services is being realized by organizations looking to build efficient machine-learning data models. Rather than developing in-house expertise, companies are finding that they are better served by outsourcing their annotation work to qualified third-party experts. TagX has extensive experience providing a variety of data annotation, cleansing, and enrichment services to its global clients. Want to know how data labeling could benefit your business? Please contact us anytime.